Sample No63 concentrate
Visual description
Dense, easily deformable, non-sticky, specific odor, slightly oily
DSC– differential scanning calorimetry (change in heat flow with temperature)
This % defining analysis was previously used, but with increasing concentration the method is too sensitive, which is illustrated by many peaks at 140 ° C.
Therefore, TGA (thermogravimetric method) will hence be used, in which the change in mass of the material was determined. Compared to the previous method, the material was not damaged but converted to melted state by determining the melting point, but the TGA method is a material destruction method, thus the material gets damaged. Each substance has its own temperature at which the structure collapses or, more precisely, becomes not functional, making it possible to determine the mass fraction of each substance in the material from the total mass that was initially introduced.
The question here is, have you used any additives, or is there a possibility of any substance entering the press? Given that the largest amount in the composition should be muscimol, the largest peak appears from 536.97 ° C to 695.08 ° C, and using the law of mass loss, we can calculate each component (see Table 1), but the device offers the possibility to determine immediately in this range how much weight is lost, which is the loss of muscimol, respectively (8.5%). The temperature of destruction is not mentioned anywhere in the scientific literature, so an actual hypothesis has been put forward here, to the exclusion of other variants. The TGA method has a limited ability to determine the destruction temperatures of the other components because there is no theoretical information that can overlap.
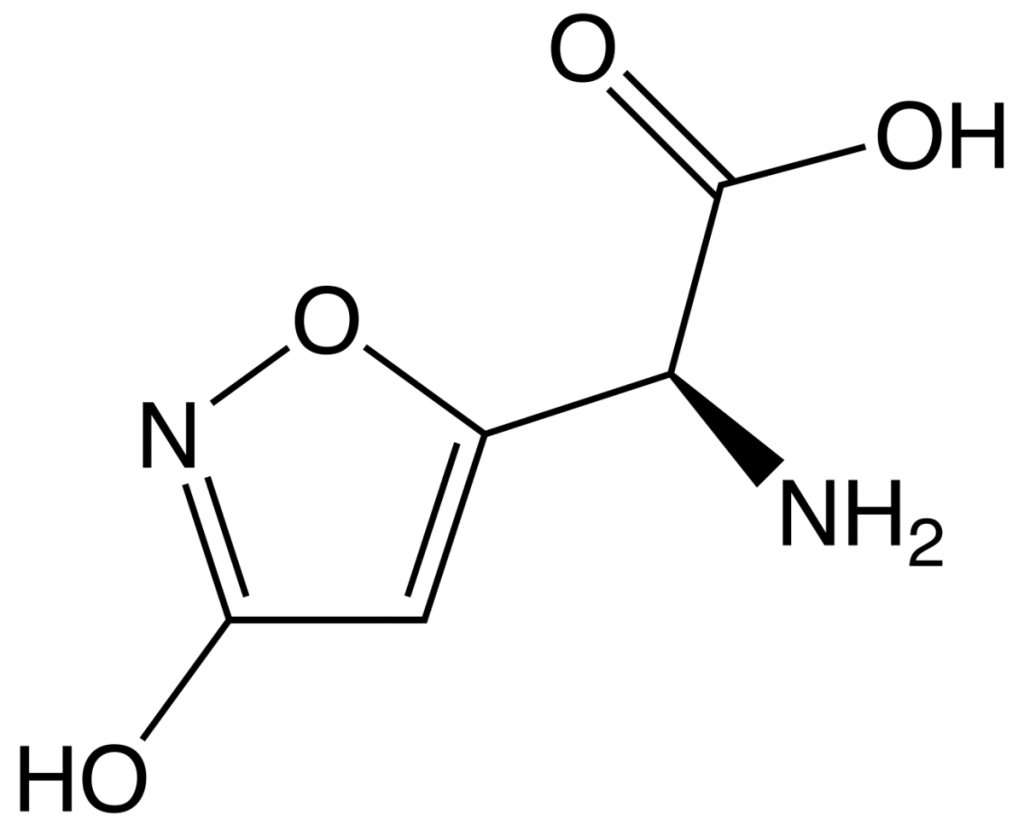
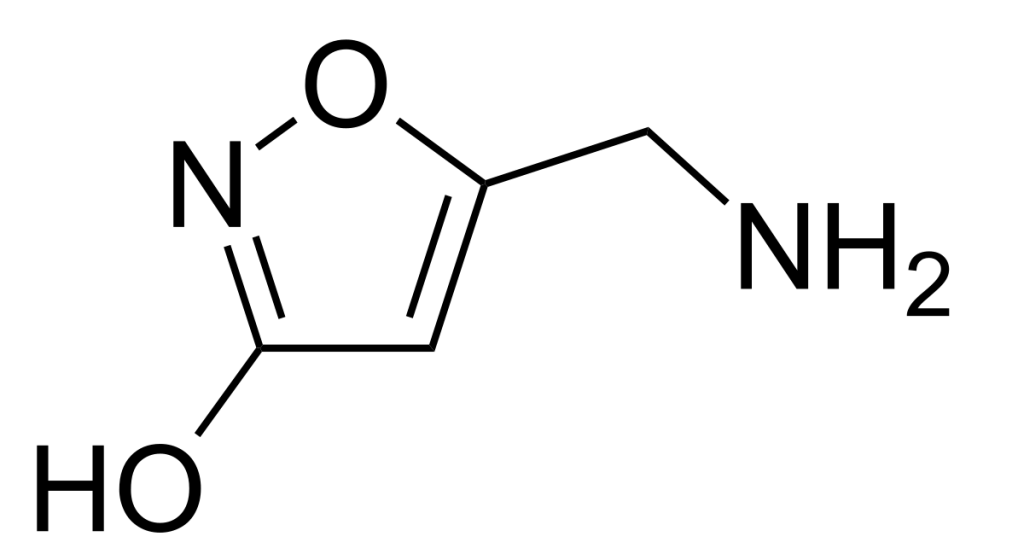
Muscimol
| NAME: | Muscimol |
| CHEMICAL NAME: | 5- (Aminomethyl) -3 (2H) -isoxazolone |
| ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES: | 5- (aminomethyl) -3-isoxazolol, 5-aminomethyl-3-hydroxyisaxazole |
| ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES: | 3-hydroxy-5-aminomethylisoxazole; agarin, pantherine |
| CHEMICAL FORMULA | C4H6N2O2 |
| MELTING POINT | 175 ° (crystals) (DSC) |
| DESTRUCTION TEMPERATURE | 600 ° C (Information obtained by us) |
Given the possible presence of ibotenic acid in the DSC data (see Figure 3), its assumption may be negligible if the correct acquisition conditions were observed.
Ibotenic acid
| NAME: | Ibotenic Acid |
| CHEMICAL NAME: | alpha-Amino-2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-5-iso-xazoleacetic acid |
| ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES: | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazoleacetic acid |
| ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES: | amino- (3-hydroxy-5-isoxazolyl) acetic acid |
| CHEMICAL FORMULA | C5H6N2O4 |
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT | 158.11 |
| MELTING POINT | 151-152 ° (anhydrous crystals) |
| MELTING POINT | 144-146 ° (monohydrate crystals) |
Muscatone
| NAME: | Muscazone |
| CHEMICAL NAME: | alpha-Amino-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-oxazoleacetic acid |
| ALTERNATE CHEMICAL NAMES: | alpha-amino-2-oxo-4-oxazoline-5-acetic acid |
| CHEMICAL FORMULA | C5H6N2O4 |
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT | 158.11 |
As such, there are many different other substances in mushrooms that qualify as nutrients: vitamins A; B1B2; C; D1, PP. Mushrooms also contain minerals: potassium, phosphorus, iron; trace elements: zinc, copper, magnesium, iodine. Mushrooms are also rich in extracts. Of course, in the case of fly agaric, it is worth mentioning the pigment that gives red color. This means that both valuable substances and muscimol are ingested at the same time when consuming such a product.
Conclusion: Muscimol content 8.5% in a specific sample No63 concentrate.
2/14/2022