How to Improve Vision Naturally: The Hidden Power of Golden Chanterelle Capsules
In an era defined by blue light screens and digital fatigue, our eyes are under constant siege. While modern medicine offers corrective solutions, many seekers of holistic wellness are asking a fundamental question: How to improve vision naturally?
The answer may lie deep within the forest floor. While many associate mushrooms solely with culinary delight or stress relief, the Golden Chanterelle (Cantharellus cibarius) holds a specific, potent profile of vitamins and amino acids that have been traditionally revered for enhancing eyesight and combating night blindness.
As the Amanita Scholar, I invite you to explore the intersection of ancient fungal wisdom and modern nutritional science.
The Problem: Digital Strain and Nutritional Gaps
Our eyes require specific nutrients to repair retinal damage and maintain visual acuity in low light. A deficiency in Vitamin A, specifically, is a primary cause of night blindness (nyctalopia) and dry eyes. While synthetic supplements exist, the body often struggles to absorb them efficiently.
This is where the Golden Chanterelle steps in—a natural, bioavailable source of vision-supporting compounds.
Mechanism of Action: The Science of the Golden Chanterelle
To understand chanterelle mushroom vision benefits, we must look at their chemical composition. Unlike the psychoactive compounds found in other species, Chanterelles are nutritional powerhouses.
1. Natural Vitamin A & Beta-Carotene
Chanterelles are famously rich in carotenoids, particularly beta-carotene, which the body converts into Vitamin A. This vitamin is essential for the formation of rhodopsin, a pigment in the retina that helps the eye adapt to low-light conditions.
2. Ergosterol (Vitamin D2)
High levels of ergosterol in Chanterelles convert to Vitamin D2. Emerging studies suggest Vitamin D plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation in the eyes and supporting age-related macular health.
3. Polysaccharides and Immune Support
Like many medicinal fungi, Chanterelles are rich in polysaccharides. These long-chain carbohydrates modulate the immune system and reduce oxidative stress, which contributes to cellular aging in the eye and skin.
Read more about this mechanism here: Polysaccharides & Beta-Glucans: The Science of Mushroom Potency
4. Golden Chanterelle Skin Rejuvenation
The same antioxidants that protect the eyes also support the skin. The high mineral content (copper and potassium) combined with amino acids aids in maintaining skin elasticity and hydration, making Chanterelles a dual-purpose ally for beauty and vision.
—
A Note on Functional Mushroom Safety: Muscimol & Ibotenic Acid
At Calm Mushroom, we believe in total transparency regarding fungal chemistry. While Chanterelles are purely nutritional, our flagship work involves the Amanita Muscaria. It is vital to understand the difference in compounds when exploring the wider world of functional mushrooms.
While Chanterelles nourish the body with vitamins, Amanita Muscaria interacts with the nervous system.
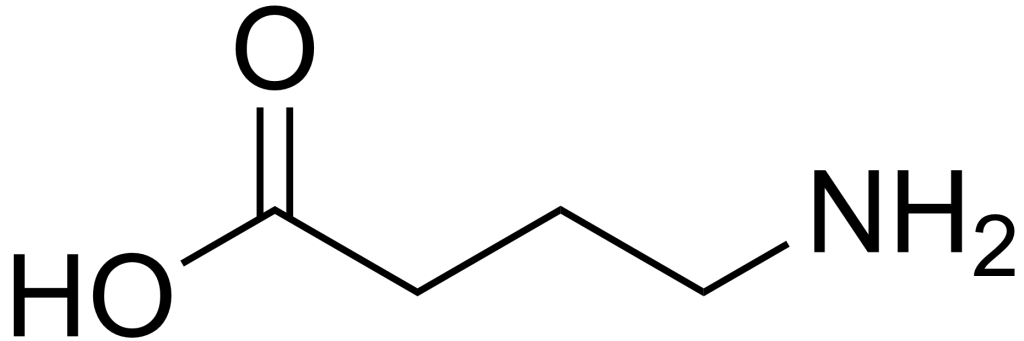
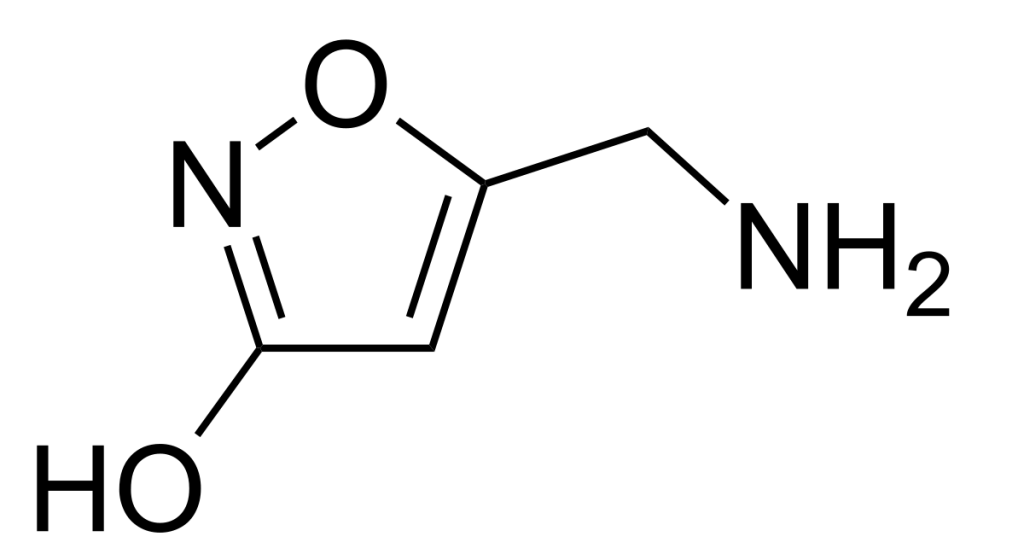
* Ibotenic Acid: In raw Amanita mushrooms, this compound is neurotoxic and can cause agitation.
Decarboxylation (The Safety Key):** Through a meticulous process of heat and drying (decarboxylation), Ibotenic Acid is converted into *Muscimol.
Muscimol:** This is the desired active compound. It acts as a potent agonist for *GABA-A receptors in the brain. Because it mimics the body’s natural GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), it promotes profound relaxation, restorative sleep, and anxiety relief without the agitation of Ibotenic Acid.
Always prioritize safety. Whether consuming Chanterelles for vision or Amanita for sleep, understanding the preparation method is the difference between a remedy and a risk.
—
Traditional vs. Modern Use
The Forest Gold
Historically, in European and Russian folklore, Chanterelles were not just prized for their apricot-like aroma but were prescribed as a folk remedy for “night blindness” and respiratory infections. They were seen as a tonic for the liver and the eyes.
Learn more about detox properties here: The Best Mushroom for Liver Health: How Golden Chanterelle Supports Detox and Restoration
Modern Application
Today, we utilize supplements for eye health that concentrate these benefits. Dried and encapsulated Chanterelle powder ensures a consistent dose of carotenoids without the need for daily foraging.
—
Holistic Support: Restoring the Eyes Through Sleep
While Golden Chanterelles provide the building blocks* for eye health (Vitamin A), your body performs the actual *repair work while you sleep. Lack of sleep increases eye strain and prevents retinal recovery.
Therefore, a truly holistic approach to improving vision involves combining nutrient intake with deep, restorative rest. For this, we recommend our specialized Amanita Muscaria products to calm the mind and ensure your body can utilize the nutrients you provide it.
Product Recommendations
1. For Deep Rest & Recovery (Liquid Format)
To ensure you get the sleep necessary for eye repair, consider our water-based extract.
* Recommendation: Calm Mushroom Extract
2. For Consistent Mood & Balance
If stress is causing physical tension (including eye strain), consistent microdosing can help regulate your nervous system.
* Recommendation: Calm Mushroom Microdosing Capsules
3. For Traditional Preparation
For those who prefer the ritual of preparing their own tea or formulations.
* Recommendation: Dried Amanita Muscaria Caps
4. Versatile Daily Use
A versatile powder that can be added to smoothies or foods for general wellness.
* Recommendation: Calm Mushroom Powder
—
FAQ: Natural Vision Improvement
Q: Can Golden Chanterelles cure blindness?
A: No. While they contain natural vitamin A for eyes which supports retinal health and can improve night vision significantly in those with deficiencies, they cannot reverse structural blindness or severe genetic conditions.
Q: How long does it take to see results?
A: Natural remedies work with the body’s metabolic cycles. Consistent supplementation over 4-8 weeks is typically required to notice improvements in night vision or reduction in eye fatigue.
Q: Are there side effects to Chanterelle capsules?
A: Chanterelles are culinary mushrooms and are generally very safe. However, always consult your physician before starting new supplements for eye health, especially if you are pregnant or on medication.
Q: Why do you mention Amanita Muscaria in a Chanterelle article?
A: We believe in a full-spectrum approach. Chanterelles provide the nutrients*, while Amanita Muscaria (via Muscimol) provides the *rest required for those nutrients to work effectively.
—
Conclusion
To improve vision naturally, we must look beyond simple eye drops. It requires a synergy of proper nutrition—specifically the rich carotenoids found in Golden Chanterelles—and the restorative power of deep sleep.
By integrating the ancient wisdom of the Chanterelle with the calming science of Amanita Muscaria, you create a biological environment where your eyes can heal, sharpen, and thrive.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational purposes only and has not been evaluated by the FDA. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Curious about the history of these botanical allies?
Check out our curated list of reading materials: Top 10 Essential Books on Amanita Muscaria: History, Identification & Traditional Uses